is 30 a good sample size for quantitative research|research sampling and sample size determination a practical application : discount store Determining an appropriate sample size is vital in drawing realistic conclusions from research findings. Although there are several widely adopted rules of thumb to calculate sample size,.
1 dia atrás · The youth-adapted problem gambling screen (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 4th Edition - Multiple Response Juvenile (DSM-IV-MR-J)) .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBMédicos pelo Brasil
Visually assess whether a normal approximation is appropriate (and ask whether an approximation is even really needed). If generating samples for research and an approximation is obligatory, generate enough of a sample size to make the approximation as close as desired .I'm currently working on a quasi-experimental research paper. I only . Summary: 40 participants is an appropriate number for most quantitative studies, but there are cases where you can recruit fewer users.
“A minimum of 30 observations is sufficient to conduct significant statistics.” This is open to many interpretations of which the most fallible one is that the sample size of 30 is enough to trust your confidence interval.
Most statisticians agree that the minimum sample size to get any kind of meaningful result is 100. If your population is less than 100 then you really need to survey all of them. A good maximum sample size is usually 10% as long as it . Determining an appropriate sample size is vital in drawing realistic conclusions from research findings. Although there are several widely adopted rules of thumb to calculate sample size,. Determining a good sample size for quantitative research. Sample size, as we’ve seen, is an important factor to consider in market research projects. Getting the sample size right will result in research findings you can .
Introduction. There are disagreements within the academic literature regarding minimum sample size for a quantitative instrument-based study, such as those using Likert .When the effect size is 1, increasing sample size from 8 to 30 significantly increases the power of the study. Yet, even 30 samples are not sufficient to reach a significant power value if effect .In general, a good sample size is one that accurately represents the population and allows for reliable statistical analysis. Larger sample sizes are typically better because they reduce the likelihood of sampling errors and provide a more .The easiest way to define your sample size is using a sample size calculator, or you can use a manual sample size calculation if you want to test your math skills. Cochran’s formula is perhaps the most well known equation for calculating .
Researchers often find it difficult to justify their sample size (i.e., a number of participants, observations, or any combination thereof). In this review article six possible approaches are discussed that can be used to justify the sample size in a quantitative study (see Table 1).This is not an exhaustive overview, but it includes the most common and .
what is a statistically significant sample size
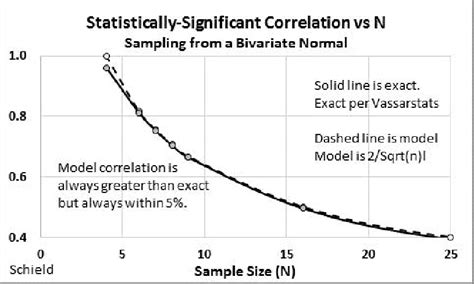
Keywords: methods, research, sample size, statistics. Introduction. . to anticipate the problem of non-response and then to make up for it by recruiting more subjects on top of the minimum sample size, usually by 20% to 30%. If, for example, the researcher is expecting a high non-response rate in a self-administered survey, then he/she should . The determination of sample size in qualitative research introduces a unique and multifaceted challenge, setting it apart from the more structured methodology of quantitative research.
Dry Oven for Persptrometer distribution
Large sample size: Quantitative research often involves collecting data from a large sample of individuals or groups in order to increase the reliability and generalizability of the findings. Objective approach: Quantitative research aims to be objective and impartial in its approach, focusing on the collection and analysis of data rather than . 1. Convenience sampling. A convenience sample simply includes the individuals who happen to be most accessible to the researcher. This is an easy and inexpensive way to gather initial data, but there is no way to tell if the sample is representative of the population, so it can’t produce generalizable results. Convenience samples are at risk for both sampling bias .How to Calculate a Statistically Significant Sample Size in Research Determining Sample Size for Probability-Based Surveys and Polling Studies. . (500/30*100 = 1,666). Determining Sample Size for Controlled Surveys. . A significance level of .05 is a good starting point, but you may adjust this number up or down depending on the aim of your .
The sample size for a study needs to be estimated at the time the study is proposed; too large a sample is unnecessary and unethical, and too small a sample is unscientific and also unethical. The necessary sample size can be calculated, using statistical software, based on certain assumptions. If n . One of the major issues in planning a research is the decision as to how a sample and the method to be employed to select the estimated sample in order to meet the objective of the research. Other rules of thumb include Harris’s (1975) difference rule (accounting for model variations) based on N > 50 + 8m, where N is the sample size, 50 is the base sample, and 8m is the adjustment of sample based on the number of predictors; Kline’s (2005, 2016) sample size range for small (less than 100), medium (100–200), and large (more .
sample size formula pdf
Sample size is the number of observations or individuals included in a study or experiment. It is the number of individuals, items, or data points selected from a larger population to represent it statistically. The sample size is a crucial consideration in research because it directly impacts the reliability and extent to which you can generalize those findings to the .The sample size is central in quantitative research, as the findings should be able to be generalised for the wider population.10 The data analysis can be done manually or more complex analyses performed using computer software sometimes with advice of a statistician. From this analysis, results like mode, mean, median, p value, CI and so on .
For example, the curve for the sample size of 20 indicates that the smaller design does not achieve 90% power until the difference is approximately 6.5. If increasing the sample size is genuinely cost prohibitive, perhaps accepting 90% power for a difference of 6.5, rather than 5, is acceptable.Sample Size for Qualitative Research in COA Development and Validation Helen Doll, MSc DPhil . Calculating sample size for quantitative studies Sample size for qualitative studies Random sampling Determining concept saturation quantitatively . • One review identified that samples of 20 and 30 (and multiples of 10) were most common (Mason .
DELİCE / The Sampling Issues in Quantitative Research • 2007 The Size of the Sample The distribution of the investigated theses in terms of their sample sizes are presented in Table 5. In an effort to increase reliability, 30% of the theses keep sample sizes as big as possible (more than 250). On the
Statistically, you need 30 to get a good fit the normal curve; 15 for a rough fit to the normal curve; 6 to be able to show enough difference for a non-parametric Wilcoxon paired t-test, or a . A good sample size will satisfy your criteria for accuracy in quantitative research results. . How do you justify a small sample size in quantitative research? A small sample size can be justified when: The .
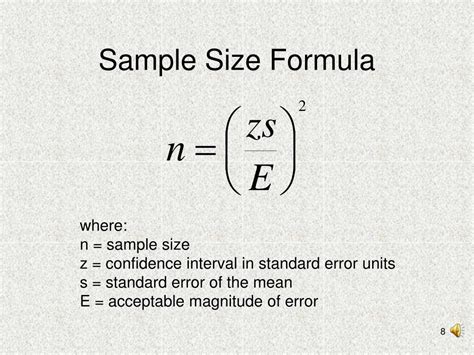
The research take the size shoe of all high school students that play basketball "officially" (that are part of the basketball team in the school). . A sample size of 30 of is considered to be . Choose an appropriate significance level (alpha value). An alpha value of p = .05 is commonly used. This means that the probability that the results found are due to chance alone is .05, or 5%, and 95% of the time a difference found between the control group and the experimental group will be statistically significant and due to the manipulation or treatment.
Sample Size and its Importance in Research Chittaranjan Andrade ABSTRACT The sample size for a study needs to be estimated at the time the study is proposed; too large a sample is unnecessary and unethical, and too small a sample is unscientific and also unethical. The necessary sample size can be calculated,
sample size for research pdf
A target sample size of at least 10 completed interviews was planned based on the likelihood of saturation and given our research goals and sampling strategy [33]. Rapid qualitative methods were . Gale Academic OneFile includes Sample size in quantitative research: Sample size will by Susan B. Fowler and Valerie Lapp. Click to explore. Use this link to get back to this page.
Ideally 30+ Often around 5. Level of Contact with Users. Less direct & more remote (e.g., analytics) . What is a good sample size for quantitative research? In quantitative research, determining a good sample size is crucial for the reliability of the results. William Hudson, CEO of Syntagm, emphasizes the importance of statistical .Statisticians have devised quantitative ways to find a good sample size. You want a large enough sample to have a reasonable chance of detecting a meaningful effect when it exists but not too large to be overly expensive. . consider your sample size carefully. Your research’s integrity depends on it. Consequently, the effort to achieve an .
To have a good sample size, researchers prefer to have multiplier of 10 e.g. for questionnaire having 30 questions/items multiplier of 10 will determine 300 good sample size. Cite 9 Recommendations
Sample selection is a key factor in research design and can determine whether research questions will be answered before the study has even begun. Good sample selection and appropriate sample size strengthen a study, protecting valuable time, money and resources. In the context of healthcare research, poor design could lead to use of harmful practices, delays . Sample adequacy in qualitative inquiry pertains to the appropriateness of the sample composition and size.It is an important consideration in evaluations of the quality and trustworthiness of much qualitative research [] and is implicated – particularly for research that is situated within a post-positivist tradition and retains a degree of commitment to realist .
Rubbing Color fastness Tester distribution
Digital CROCKMETER distribution
web1080p. Luísa Sonza #2. 12 sec Luc4Sz - 100% -
is 30 a good sample size for quantitative research|research sampling and sample size determination a practical application